
29 Nov “Why Big Investors are still Bullish on PNB”
“Unlocking PNB’s Success: How It Overcame Key Risks”
PNB has taken center stage in the stock market, with a commendable rally in PSU banks.
It stands tall as one of India’s leading public sector banks. PNB, or Punjab National Bank, has a rich history tracing back to its establishment in 1894. Founded in Lahore, undivided India, it has played a pivotal role in the financial landscape.
Key Milestones:
- Establishment: Founded on May 19, 1894, by Lala Lajpat Rai.
- Post-Independence: After the partition in 1947, PNB became a key player in the Indian banking sector.
- Nationalization: In 1969, the bank underwent nationalization, contributing to the government’s efforts to strengthen the banking industry.
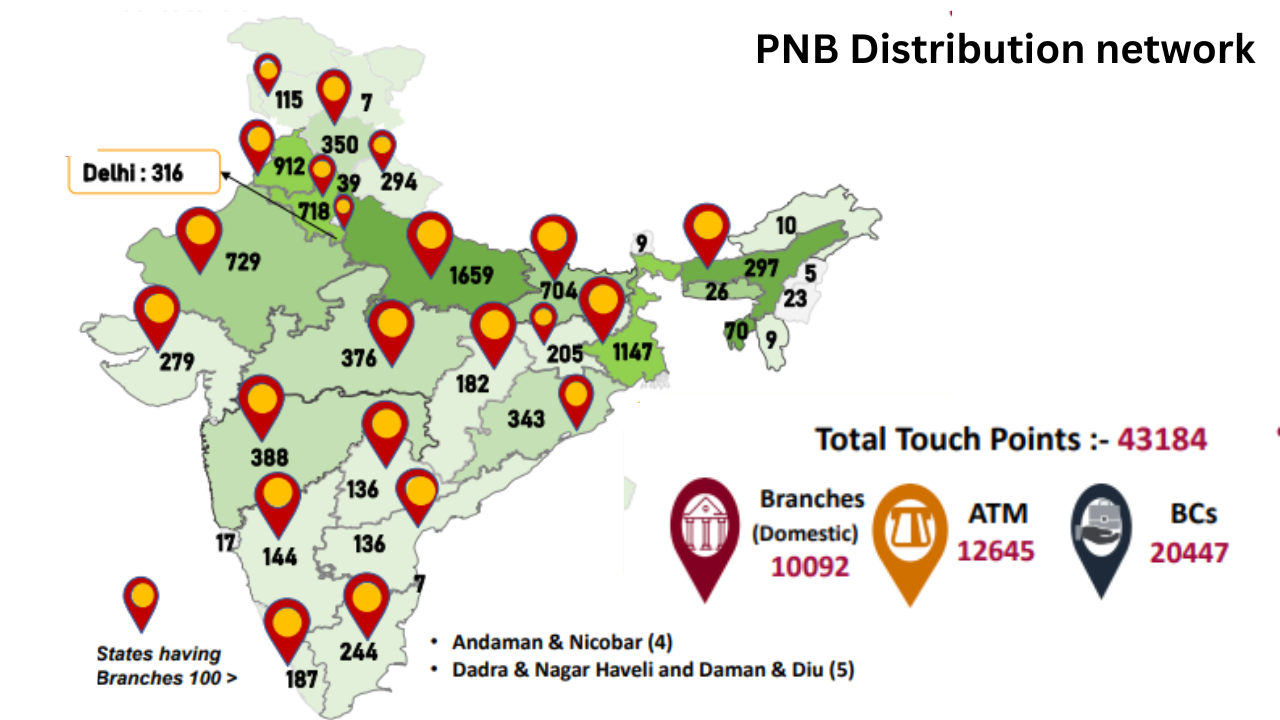
Subsidiary Businesses:
- PNB Housing Finance Ltd (32.65% stake):
- Established in 1988, this housing finance company, in which PNB holds a significant stake, provides seamless financial services through its widespread branch network.
- PNB Gilts Ltd (74% stake):
- A prominent player in the Indian debt market, PNB Gilts Ltd, in which PNB holds a substantial stake, plays a crucial role in fortifying the domestic fixed income markets. It boasts a high market share in overall trading turnover.
- PNB Metlife India Insurance Co. Ltd (30% stake):
- A leading life insurance company, PNB Metlife operates across 107 locations in India, serving over 100 million customers in more than 11,000 locations. It has strategic partnerships with PNB, Jammu & Kashmir Bank, and Karnataka Bank Ltd for the distribution of insurance policies.
Related Read: “From Crisis to Confidence: YES Bank’s Journey to Stability”
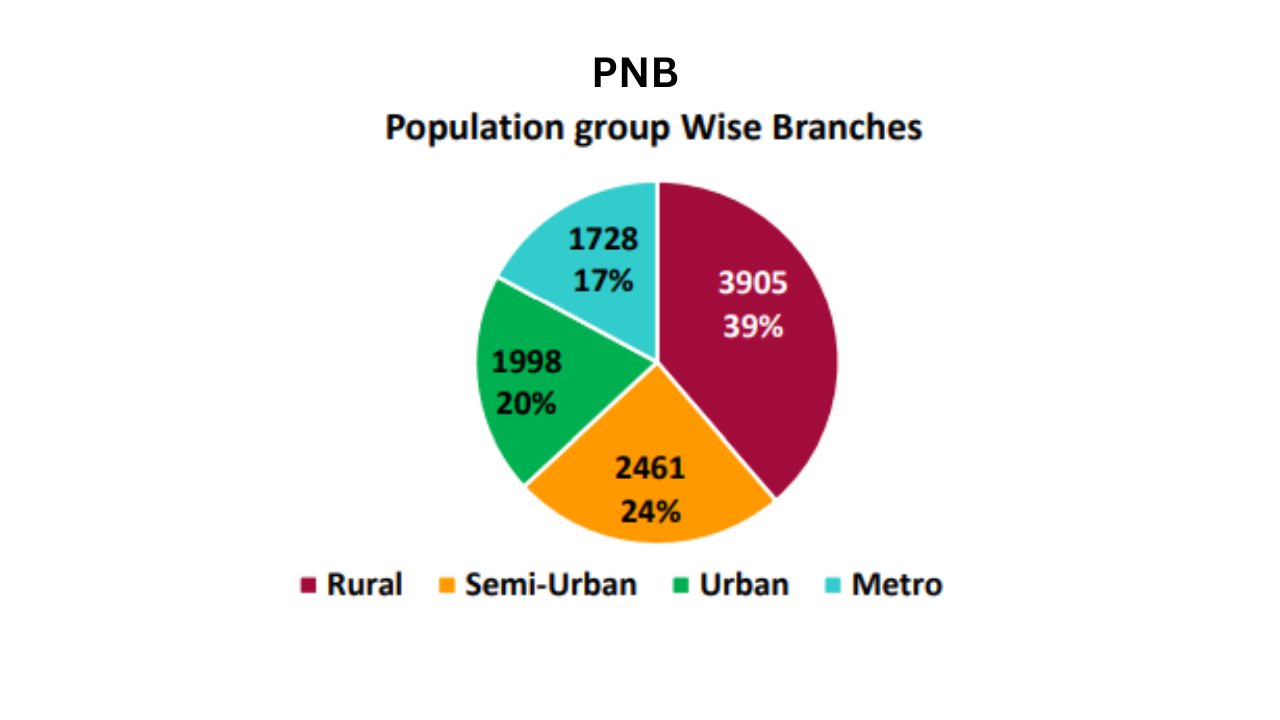
Services Offered: PNB caters to a diverse clientele with a wide array of services, including:
- Retail Banking: Providing services like savings accounts, loans, and fixed deposits.
- Corporate Banking: Offering financial solutions to businesses of all sizes.
- Digital Banking: Embracing technology for online transactions, mobile banking, and digital services.
- International Presence: Extending its reach globally with a network of branches and services.
Merger with OBC and UBI:
- Oriental Bank of Commerce and United Bank of India merged with PNB from April 1, 2020.
- As per the scheme, shareholders of both banks were allotted ~535 crores worth of equity shares.
Qualified Institutional Placement (QIP):
- In December 2020, the bank aimed to raise ~7,000 crores through QIP but fell short by 46%, issuing equity capital of ~213 crores for a consideration of ~₹3,800 crores.
- In 2021, an additional ₹1,800 crores were raised via QIP at ₹33.75 per share.
Regional Rural Banks (RRBs): The bank collaborates with various RRBs across India, including Punjab Gramin Bank, Himachal Pradesh Gramin Bank, and Tripura Gramin Bank, contributing to a combined business of approximately ~1,70,000 crores.
Also Read: “Suzlon 2.0: What Lies Ahead -Post Turnaround?”
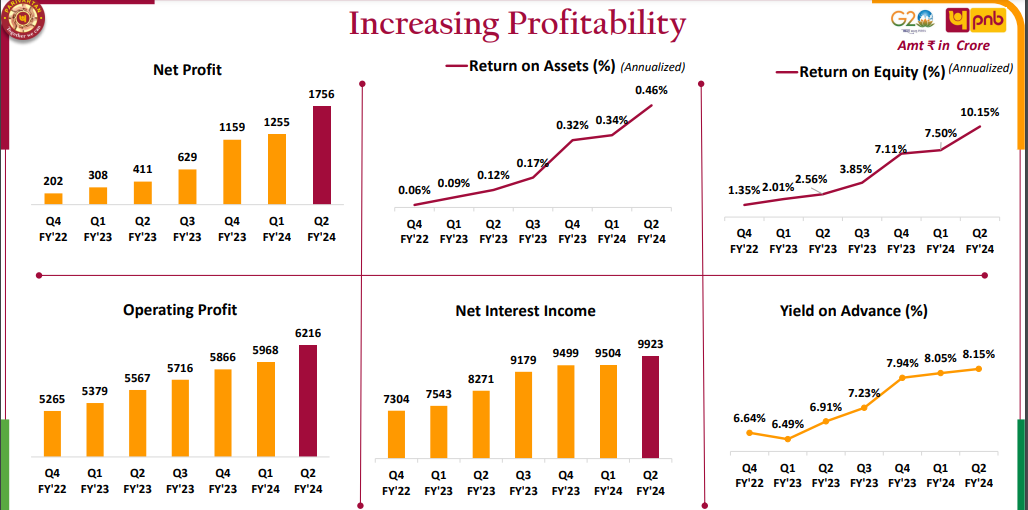
Financial Performance:
PNB has witnessed a remarkable upswing in its financial indicators over the past 14 quarters post-amalgamation:
- Net Interest Income: Achieved the highest in 14 quarters.
- Operating Profit: Reached its peak.
- Net Profit: Recorded the highest in the last 14 quarters.
Growth Metrics:
- Gross Business: Expanded by 11.26%.
- Deposits: Increased by 9.7%.
- Gross Advances: Grew by 13.43%.
- Savings: Grew by 4.32%.
- CASA: Increased by 2.36%.
Year-over-Year Growth:
- Net Interest Income: Witnessed a robust YoY growth of 19.97%.
- Operating Profit: Grew by 11.67%.
- Net Profit: Soared by an impressive 327.14%.

NPA and Provisioning:
- Gross NPA: Reduced to Rs. 65,000 crores.
- Net NPA: Decreased to Rs. 13,000 crores.
- Provision Coverage Ratio (PCR): Elevated to 91.91%, reducing the need for aging provisions.
Asset Quality:
- Slippages: Reduced to Rs. 1,826 crores.
- Recoveries: Achieved Rs. 5,500 crores.
Management on NPA Provisions and Recoveries:
- Anticipates a decline in NPA provisions, foreseeing increased profitability from recoveries.
- In line with future aspirations, the bank aims to achieve a 1% Return on Assets (ROA) by the conclusion of 2024-25.
Also Read: The Remarkable Turnaround of JLR: From Tata’s “Biggest Mistake” to a “Biggest Victory”
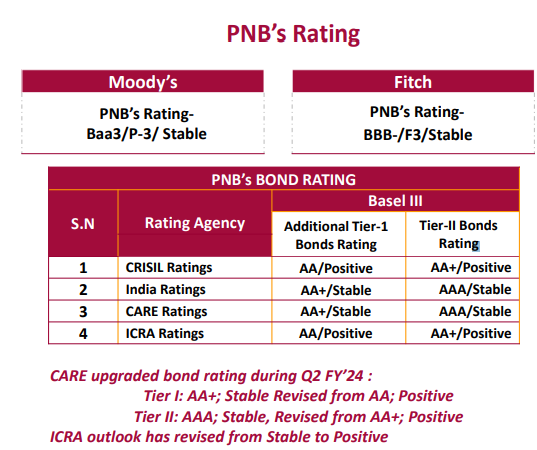
Challenges Overcome:
- In the early 2000s, PSU banks, including PNB, faced challenges in asset quality, governance, and technology.
- Today, these challenges have been overcome, reflecting adaptability and strategic foresight.
Market Performance and Expert Perspectives:
- Experts like Madhusudan Kela, Vikas Khemani, and N Jayakumar project that the momentum is far from over.
- Motilal Oswal Securities maintained its target at Rs 75, projecting a Return on Asset (RoA) of 0.6% and Return on Equity (RoE) of 9% by FY25.
- Kotak Institutional Equities commented on the impact of elevated provisions and higher retirement-related costs on PNB’s return ratios. They anticipate a decline in provisions as fresh slippages and net Non-Performing Loans (NPLs) decrease. Kotak suggests a fair value of Rs 82 for the stock.
- Nirmal Bang Institutional Equities adjusted the valuation to September 2025 adjusted book value of Rs 98.30, setting a target price of Rs 78 (previously Rs 71), indicating a 12% upside. Despite recent stock price rallies and lower return ratios, they maintain an “accumulate” stance.
- Christopher Wood’s global perspective adds a global context to PNB’s success.
Global Recognition and Changing Dynamics:
- Christopher Wood’s observation underscores global recognition.
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Act of 2016 played a pivotal role, leading to a re-rating of public sector banks in the stock market.
- Despite positive trends, questions arise about the continued outperformance of public sector banks.
- Christopher Wood suggests opportunities for new investors, particularly global funds, in India’s leading banks
Other Fundamentals
- Market Cap ₹ 86,435 Cr.
- Current Price ₹ 78.6
- High / Low ₹ 83.5 / 44.4
- Face Value ₹ 2.00
- Book Value ₹ 93.4
- Dividend Yield 0.83 %
- Stock P/E 14.6
- Industry PE 12.7
- PEG Ratio 0.82
- Return over 1year 47.1 %
- ROCE 4.10 %
- ROE 3.34 %
- Sales growth 27.1 %
- Profit growth 151 %
- OPM 56.2 %
“RBI’s Risk Weight Hike: The Impact on Banks”
The RBI’s recent move to increase risk weights on unsecured consumer loans has sparked changes in the banking sector.
Now, it has directed that the risk weight for consumer credit exposure be increased by 25 percentage points to 125%, for all commercial banks and NBFCs. This would apply to personal loans, excluding housing loans, education loans, vehicle loans, and loans secured by gold and gold jewellery.
At present, exposures in this realm mandate a risk weight of 100%.
Key Points:
- Increased Capital Requirements:
- Banks now face higher capital requirements due to the raised risk weights.
- This adjustment aims to fortify risk management and curb the proliferation of unsecured loans.
- Lending Rates and Consumer Impact:
- Higher capital requirements may compel banks to adjust lending rates upwards.
- Consumers, particularly those seeking unsecured personal loans and credit cards, could experience increased interest rates.
Key Risks Associated with PNB:
Delving into Punjab National Bank’s (PNB) landscape, it’s crucial to recognize and understand specific risks that may impact its trajectory. Let’s explore these particular challenges.
- Credit Risk:
- PNB, like any financial institution, faces credit risk, the potential of borrowers failing to meet repayment obligations.
- The recent RBI directive on increased risk weights underscores the industry-wide concern about managing credit risk, affecting PNB’s lending portfolio.
- Asset Quality Concerns:
- The reduction in gross non-performing assets (NPAs) is positive, but sustained vigilance is crucial.
- A sudden downturn in economic conditions could impact the quality of PNB’s assets, especially given its significant loan exposure.
- Operational Risks:
- Operational risks, arising from internal processes, systems, and external events, are inherent.
- PNB’s digital transformation may expose it to cyber threats, emphasizing the importance of robust cybersecurity measures.
- Regulatory and Compliance Risks:
- Regulatory changes, such as the recent RBI directives, introduce compliance challenges.
- PNB must stay abreast of evolving regulations to ensure adherence and avoid penalties.
Understanding these specific risks allows stakeholders to navigate PNB’s journey more effectively.
While PNB has demonstrated resilience, ongoing risk management, and strategic foresight will be pivotal in mitigating these challenges and sustaining long-term success.
Please note that we are not SEBI-registered advisors or analysts. All the views shared in this article and all the content shared on aceink.com are only for learning and educational purposes. Any part of the article or any information on Aceink.com should not be interpreted or considered as investment advice. None of the opinions, views, or content posted on Aceink.com constitutes investment advice, as we are not SEBI-registered advisors or analysts.
DISCLAIMER:
We are not SEBI-registered advisors or analysts. All the views shared in this article and all the content shared on aceink.com are only for learning and educational purposes. Any part of the article or any information on Aceink.com should not be interpreted or considered as investment advice. None of the opinions, views, or content posted on Aceink.com constitutes investment advice, as we are not SEBI-registered advisors or analysts.
Aceink.com or any person associated with this website accepts no liability or responsibility for any direct, indirect, implied, or any other consequential damages arising directly or indirectly due to any action taken based on the information provided on this website. Please conduct your own research, and we suggest seeking investment advice only from a SEBI-registered investment advisor.
The views expressed by investment experts, broking houses, news and media houses, rating agencies, etc., are their own and not those of Aceink.com or its management. Aceink.com advises users to consult a SEBI-registered investment advisor before making any decisions.






No Comments